DevOps is one of the hottest buzzwords in tech now, although it is much more than buzz. It is a collaboration between the development and operations team, where they work together to deliver a product faster and efficiently. In the past few years, there has been a tremendous increase in job listings for DevOps engineers. Multinational companies, like Google, Facebook, and Amazon, frequently have multiple open positions for DevOps engineer Experts. However, the job market is highly competitive, and the questions asked in a DevOps engineer interview can cover a lot of challenging subjects.
If you’ve completed your DevOps Course and started to prepare for development and operations roles in the IT industry, you know it’s a challenging field that will take some real preparation to break into. Here are some of the most common DevOps interview questions and answers that can help you while you prepare for DevOps roles in the industry.
What is DevOps?
To improve the efficiency and quality of software development, delivery, and deployment, a group of activities and approaches called DevOps combines software development (Dev) with information technology operations (Ops).
DevOps' primary objective is to foster teamwork between the development and operations teams so that they may collaborate easily across the whole software development life cycle. In addition, automation, continuous integration, delivery, and deployment are used to speed up and reduce mistakes in the software development process.
Monitoring and feedback are also emphasized in DevOps, which enables the development and operations teams to see problems early and proactively handle them. Using DevOps methods, businesses may improve their agility, competitiveness, and overall productivity by achieving quicker release cycles, higher-quality software, and enhanced team cooperation.
What is a DevOps Engineer?
An expert in developing, deploying, and maintaining software systems with DevOps methodology and practices is known as a DevOps engineer.
DevOps engineers collaborate closely with IT operations teams, software developers, and other stakeholders to guarantee the effective delivery of software products. To increase the efficiency and quality of software development, they are in charge of implementing automation, continuous integration, and continuous delivery/deployment (CI/CD) practices. They also locate and resolve issues that arise throughout the development process.
DevOps engineers often have extensive backgrounds in IT operations, systems administration, software development, scripting, automation, and cloud computing skills. In addition to source code management systems, build and deployment tools, virtualization and container technologies, and monitoring and logging tools, they are adept at using various tools and technologies.
DevOps engineers need to be proficient in technical and interpersonal skills, teamwork, and problem-solving techniques. In addition, they must be able to interact and collaborate successfully with coworkers from all backgrounds and disciplines since they work closely with several teams within the business.
What are the Requirements to Become a DevOps Engineer?
Depending on the business and the individual function, different criteria for becoming a DevOps engineer may exist. However, some specific fundamental skills and certifications are frequently needed or recommended. They consist of the following:
- Excellent technical background: DevOps engineers should be well-versed in IT operations, systems administration, and software development. Having a degree in computer science background, information technology, or a similar discipline may be required, as well as relevant experience and certifications.
- Experience with DevOps tools and methodologies: DevOps engineers should have experience with various DevOps technologies and processes, including version control systems, build and deployment automation, containerization, cloud computing, and monitoring and logging tools.
- Scripting and automation skills: DevOps engineers should have strong scripting skills and be proficient in using tools such as Bash, Python, or PowerShell to automate tasks and processes.
- Cloud computing experience: DevOps engineers should have experience working with cloud platforms such as Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, or Google Cloud Platform (GCP).
- Soft skills: DevOps engineers should be effective communicators, able to work collaboratively with teams across different departments, and possess strong problem-solving and analytical skills.
- Certification: Some organizations may require DevOps engineers to hold relevant certifications such as Certified DevOps Engineer (CDE), Certified Kubernetes Administrator (CKA), or AWS Certified DevOps Engineer - Professional.
Let us now begin with some general DevOps interview questions and answers.
General DevOps Interview Questions
1. What do you know about DevOps?
Your answer must be simple and straightforward. Begin by explaining the growing importance of DevOps in the IT industry. Discuss how such an approach aims to synergize the efforts of the development and operations teams to accelerate the delivery of software products, with a minimal failure rate. Include how DevOps is a value-added practice, where development and operations engineers join hands throughout the product or service lifecycle, right from the design stage to the point of deployment.
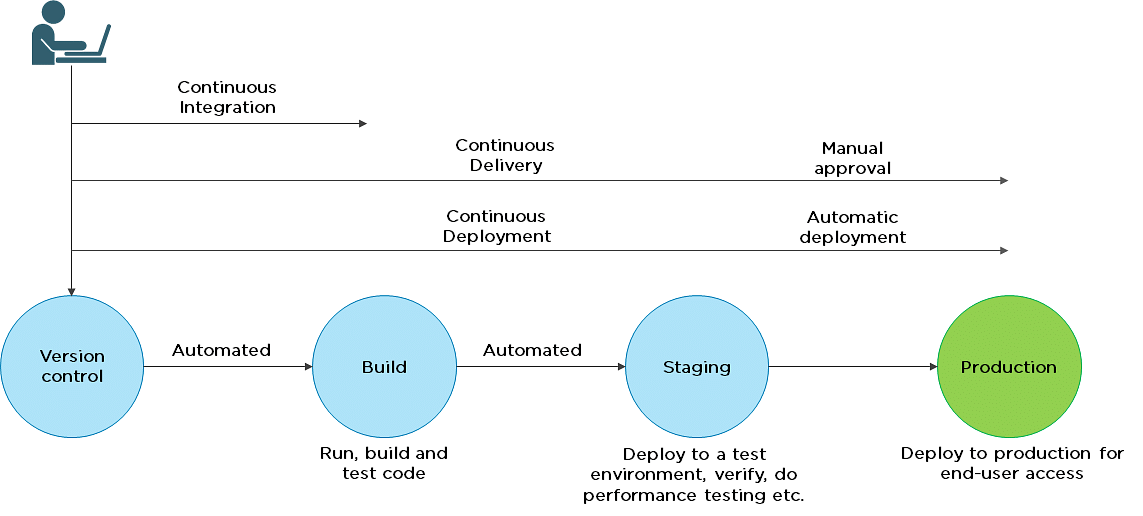
2. How is DevOps different from agile methodology?
DevOps is a culture that allows the development and the operations team to work together. This results in continuous development, testing, integration, deployment, and monitoring of the software throughout the lifecycle.
Agile is a software development methodology that focuses on iterative, incremental, small, and rapid releases of software, along with customer feedback. It addresses gaps and conflicts between the customer and developers.
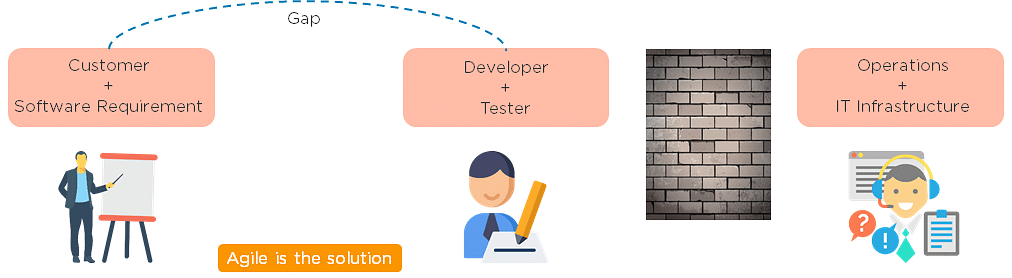
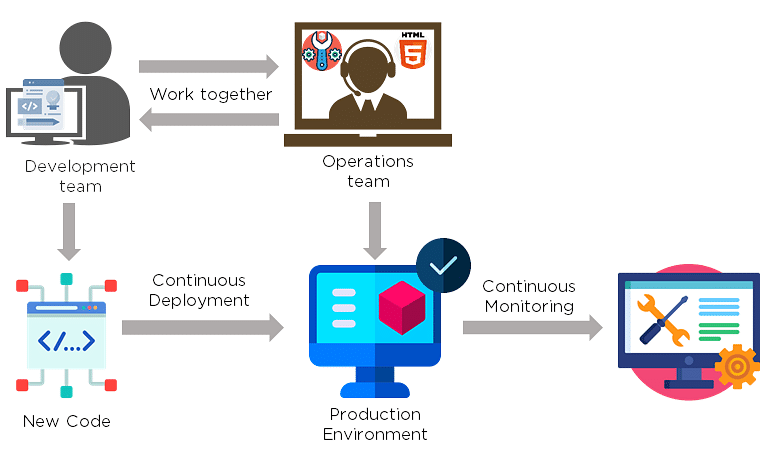
DevOps addresses gaps and conflicts between the Developers and IT Operations.
3. Which are some of the most popular DevOps tools?
The most popular DevOps tools include:
4. What are the different phases in DevOps?
The various phases of the DevOps lifecycle are as follows:
- Plan: Initially, there should be a plan for the type of application that needs to be developed. Getting a rough picture of the development process is always a good idea.
- Code: The application is coded as per the end-user requirements.
- Build: Build the application by integrating various codes formed in the previous steps.
- Test: This is the most crucial step of the application development. Test the application and rebuild, if necessary.
- Integrate: Multiple codes from different programmers are integrated into one.
- Deploy: Code is deployed into a cloud environment for further usage. It is ensured that any new changes do not affect the functioning of a high traffic website.
- Operate: Operations are performed on the code if required.
- Monitor: Application performance is monitored. Changes are made to meet the end-user requirements.
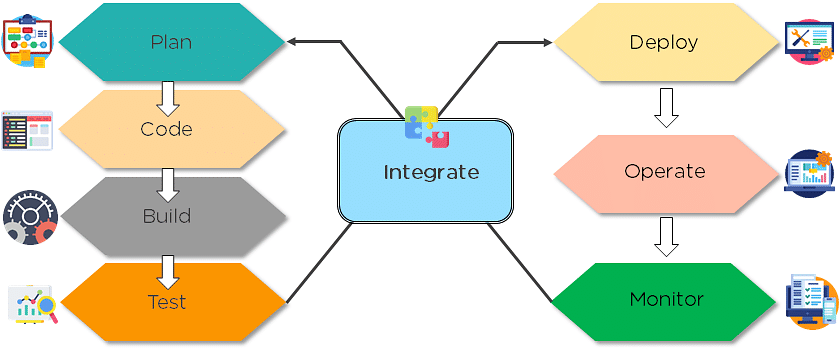
The above figure indicates the DevOps lifecycle.
5. Mention some of the core benefits of DevOps.
The core benefits of DevOps are as follows:
Technical benefits
- Continuous software delivery
- Less complex problems to manage
- Early detection and faster correction of defects
Business benefits
- Faster delivery of features
- Stable operating environments
- Improved communication and collaboration between the teams
Also Read: How to Become a DevOps Engineer?
6. How will you approach a project that needs to implement DevOps?
The following standard approaches can be used to implement DevOps in a specific project:
Stage 1
An assessment of the existing process and implementation for about two to three weeks to identify areas of improvement so that the team can create a road map for the implementation.
Stage 2
Create a proof of concept (PoC). Once it is accepted and approved, the team can start on the actual implementation and roll-out of the project plan.
Stage 3
The project is now ready for implementing DevOps by using version control/integration/testing/deployment/delivery and monitoring followed step by step.
By following the proper steps for version control, integration, testing, deployment, delivery, and monitoring, the project is now ready for DevOps implementation.
7. What is the difference between continuous delivery and continuous deployment?
Continuous Delivery |
Continuous Deployment |
| Ensures code can be safely deployed on to production | Every change that passes the automated tests is deployed to production automatically |
| Ensures business applications and services function as expected | Makes software development and the release process faster and more robust |
| Delivers every change to a production-like environment through rigorous automated testing | There is no explicit approval from a developer and requires a developed culture of monitoring |
8. What is the role of configuration management in DevOps?
- Enables management of and changes to multiple systems.
- Standardizes resource configurations, which in turn, manage IT infrastructure.
- It helps with the administration and management of multiple servers and maintains the integrity of the entire infrastructure.
9. How does continuous monitoring help you maintain the entire architecture of the system?
Continuous monitoring in DevOps is a process of detecting, identifying, and reporting any faults or threats in the entire infrastructure of the system.
- Ensures that all services, applications, and resources are running on the servers properly.
- Monitors the status of servers and determines if applications are working correctly or not.
- Enables continuous audit, transaction inspection, and controlled monitoring.
10. What is the role of AWS in DevOps?
AWS has the following role in DevOps:
- Flexible services: Provides ready-to-use, flexible services without the need to install or set up the software.
- Built for scale: You can manage a single instance or scale to thousands using AWS services.
- Automation: AWS lets you automate tasks and processes, giving you more time to innovate
- Secure: Using AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM), you can set user permissions and policies.
- Large partner ecosystem: AWS supports a large ecosystem of partners that integrate with and extend AWS services.
11. Name three important DevOps KPIs.
The three important KPIs are as follows:
- Meantime to failure recovery: This is the average time taken to recover from a failure.
- Deployment frequency: The frequency in which the deployment occurs.
- Percentage of failed deployments: The number of times the deployment fails.
12. Explain the term "Infrastructure as Code" (IaC) as it relates to configuration management.
- Writing code to manage configuration, deployment, and automatic provisioning.
- Managing data centers with machine-readable definition files, rather than physical hardware configuration.
- Ensuring all your servers and other infrastructure components are provisioned consistently and effortlessly.
- Administering cloud computing environments, also known as infrastructure as a service (IaaS).
13. How is IaC implemented using AWS?
Start by talking about the age-old mechanisms of writing commands onto script files and testing them in a separate environment before deployment and how this approach is being replaced by IaC. Similar to the codes written for other services, with the help of AWS, IaC allows developers to write, test, and maintain infrastructure entities in a descriptive manner, using formats such as JSON or YAML. This enables easier development and faster deployment of infrastructure changes.
14. Why Has DevOps Gained Prominence over the Last Few Years?
Before talking about the growing popularity of DevOps, discuss the current industry scenario. Begin with some examples of how big players such as Netflix and Facebook are investing in DevOps to automate and accelerate application deployment and how this has helped them grow their business. Using Facebook as an example, you would point to Facebook’s continuous deployment and code ownership models and how these have helped it scale up but ensure the quality of experience at the same time. Hundreds of lines of code are implemented without affecting quality, stability, and security.
Your next use case should be Netflix. This streaming and on-demand video company follow similar practices with fully automated processes and systems. Mention the user base of these two organizations: Facebook has 2 billion users while Netflix streams online content to more than 100 million users worldwide.
These are great examples of how DevOps can help organizations to ensure higher success rates for releases, reduce the lead time between bug fixes, streamline and continuous delivery through automation, and an overall reduction in manpower costs.
We will now look into the next set of DevOps Interview Questions that includes - Git, Selenium, Jenkins.
15. What are the fundamental differences between DevOps & Agile?
The main differences between Agile and DevOps are summarized below:
Characteristics |
Agile |
DevOps |
|
Work Scope |
Only Agility |
Automation needed along with Agility |
|
Focus Area |
Main priority is Time and deadlines |
Quality and Time management are of equal priority |
|
Feedback Source |
The main source of feedback - customers |
The main source of feedback - self (tools used for monitoring) |
|
Practices or Processes followed |
Practices like Agile Kanban, Scrum, etc., are followed. |
Processes and practices like Continuous Development (CD), Continuous Integration (CI), etc., are followed. |
|
Development Sprints or Release cycles |
Release cycles are usually smaller. |
Release cycles are smaller, along with immediate feedback. |
|
Agility |
Only development agility is present. |
Both in operations and development, agility is followed. |
16. What are the anti-patterns of DevOps?
Patterns are common practices that are usually followed by organizations. An anti-pattern is formed when an organization continues to blindly follow a pattern adopted by others but does not work for them. Some of the myths about DevOps include:
- Cannot perform DevOps → Have the wrong people
- DevOps ⇒ Production Management is done by developers
- The solution to all the organization’s problems ⇒ DevOps
- DevOps == Process
- DevOps == Agile
- Cannot perform DevOps → Organization is unique
- A separate group needs to be made for DevOps
17. What are the benefits of using version control?
Here are the benefits of using Version Control:
- All team members are free to work on any file at any time with the Version Control System (VCS). Later on, VCS will allow the team to integrate all of the modifications into a single version.
- The VCS asks to provide a brief summary of what was changed every time we save a new version of the project. We also get to examine exactly what was modified in the content of the file. As a result, we will be able to see who made what changes to the project.
- Inside the VCS, all the previous variants and versions are properly stored. We will be able to request any version at any moment, and we will be able to retrieve a snapshot of the entire project at our fingertips.
- A VCS that is distributed, such as Git, lets all the team members retrieve a complete history of the project. This allows developers or other stakeholders to use the local Git repositories of any of the teammates even if the main server goes down at any point in time.
18. Describe the branching strategies you have used.
To test our knowledge of the purpose of branching and our experience of branching at a past job, this question is usually asked.
Below topics can help in answering this DevOps interview question -
- Release branching - We can clone the develop branch to create a Release branch once it has enough functionality for a release. This branch kicks off the next release cycle, thus no new features can be contributed beyond this point. The things that can be contributed are documentation generation, bug fixing, and other release-related tasks. The release is merged into master and given a version number once it is ready to ship. It should also be merged back into the development branch, which may have evolved since the initial release.
- Feature branching - This branching model maintains all modifications for a specific feature contained within a branch. The branch gets merged into master once the feature has been completely tested and approved by using tests that are automated.
- Task branching - In this branching model, every task is implemented in its respective branch. The task key is mentioned in the branch name. We need to simply look at the task key in the branch name to discover which code implements which task.
19. Can you explain the “Shift left to reduce failure” concept in DevOps?
Shift left is a DevOps idea for improving security, performance, and other factors. Let us take an example: if we look at all of the processes in DevOps, we can state that security is tested prior to the deployment step. We can add security in the development phase, which is on the left, by employing the left shift method. [will be depicted in a diagram] We can integrate with all phases, including before development and during testing, not just development. This most likely raises the security level by detecting faults at an early stage.
20. What is the Blue/Green Deployment Pattern?
This is a method of continuous deployment that is commonly used to reduce downtime. This is where traffic is transferred from one instance to another. In order to include a fresh version of the code, we must replace the old code with a new code version.
The new version exists in a green environment and the old version exists in a blue environment. After making changes to the previous version, we need a new instance from the old one to execute a newer version of the instance.
21. What is Continuous Testing?
Continuous Testing constitutes the running of automated tests as part of the software delivery pipeline to provide instant feedback on the business risks present in the most recent release. In order to prevent problems in step-switching in the Software delivery life-cycle and to allow Development teams to receive immediate feedback, every build is continually tested in this manner. This results in a significant increase in speed in a developer's productivity as it eliminates the requirement for re-running all the tests after each update and project re-building.
22. What is Automation Testing?
Test automation or manual testing Automation is the process of automating a manual procedure in order to test an application or system. Automation testing entails the use of independent testing tools that allow you to develop test scripts that can be run repeatedly without the need for human interaction.
23. What are the benefits of Automation Testing?
Some of the advantages of Automation Testing are -
- Helps to save money and time.
- Unattended execution can be easily done.
- Huge test matrices can be easily tested.
- Parallel execution is enabled.
- Reduced human-generated errors, which results in improved accuracy.
- Repeated test tasks execution is supported.
24. How to automate Testing in the DevOps lifecycle?
Developers are obliged to commit all source code changes to a shared DevOps repository.
Every time a change is made in the code, Jenkins-like Continuous Integration tools will grab it from this common repository and deploy it for Continuous Testing, which is done by tools like Selenium.
25. Why is Continuous Testing important for DevOps?
Any modification to the code may be tested immediately with Continuous Testing. This prevents concerns like quality issues and releases delays that might occur whenever big-bang testing is delayed until the end of the cycle. In this way, Continuous Testing allows for high-quality and more frequent releases.
26. What are the key elements of Continuous Testing tools?
Continuous Testing key elements are:
- Test Optimization: It guarantees that tests produce reliable results and actionable information. Test Data Management, Test Optimization Management, and Test Maintenance are examples of aspects.
- Advanced Analysis: In order to avoid problems from occurring in the first place and to achieve more within each iteration, it employs automation in areas like scope assessment/prioritization, changes effect analysis, and static code analysis.
- Policy Analysis: It guarantees that all processes are in line with the organization's changing business needs and that all compliance requirements are met.
- Risk Assessment: Test coverage optimization, technical debt, risk mitigation duties, and quality evaluation are all covered to guarantee the build is ready to move on to the next stage.
- Service Virtualization: Ensures that real-world testing scenarios are available. Service visualisation provides access to a virtual representation of the needed testing phases, ensuring its availability and reducing the time spent setting up the test environment.
- Requirements Traceability: It guarantees that no rework is necessary and real criteria are met. To determine which needs require additional validation, are in jeopardy and performing as expected, an object evaluation is used.
DevOps Interview Questions for Source Code Management: Git
27. Explain the difference between a centralized and distributed version control system (VCS).
Centralized Version Control System
- All file versions are stored on a central server
- No developer has a copy of all files on a local system
- If the central server crashes, all data from the project will be lost
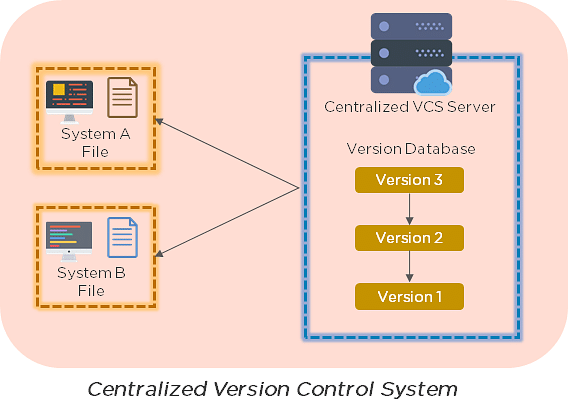
Distributed Control System
- Every developer has a copy of all versions of the code on their systems
- Enables team members to work offline and does not rely on a single location for backups
- There is no threat, even if the server crashes
28. What is the git command that downloads any repository from GitHub to your computer?
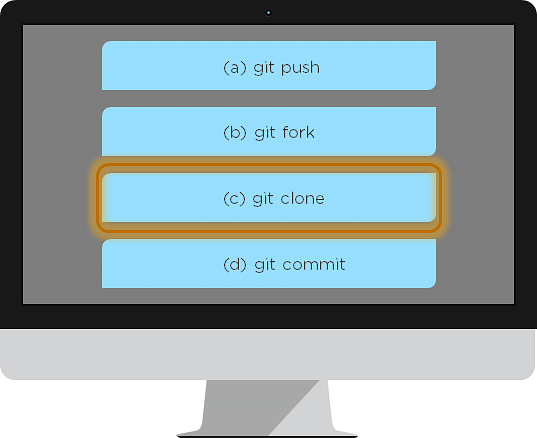
The git command that downloads any repository from GitHub to your computer is git clone.
29. How do you push a file from your local system to the GitHub repository using Git?
First, connect the local repository to your remote repository:
git remote add origin [copied web address]
// Ex: git remote add origin https://github.com/Simplilearn-github/test.git
Second, push your file to the remote repository:
git push origin master
30. How is a bare repository different from the standard way of initializing a Git repository?
Using the standard method:
git init
- You create a working directory with git init
- A .git subfolder is created with all the git-related revision history
Using the bare way
git init --bare
- It does not contain any working or checked out a copy of source files
- Bare repositories store git revision history in the root folder of your repository, instead of the .git subfolder
31. Which of the following CLI commands can be used to rename files?
- git rm
- git mv
- git rm -r
- None of the above
The correct answer is B) git mv
32. What is the process for reverting a commit that has already been pushed and made public?
There are two ways that you can revert a commit:
- Remove or fix the bad file in a new commit and push it to the remote repository. Then commit it to the remote repository using:
git commit –m "commit message"
- Create a new commit that undoes all the changes that were made in the bad commit. Use the following command:
git revert <commit id>
Example: git revert 56de0938f
33. Explain the difference between git fetch and git pull.
Git fetch |
Git pull |
| Git fetch only downloads new data from a remote repository | Git pull updates the current HEAD branch with the latest changes from the remote server |
| Does not integrate any new data into your working files | Downloads new data and integrate it with the current working files |
| Users can run a Git fetch at any time to update the remote-tracking branches | Tries to merge remote changes with your local ones |
|
Command - git fetch origin git fetch –-all |
Command - git pull origin master |
34. What is Git stash?
A developer working with a current branch wants to switch to another branch to work on something else, but the developer doesn't want to commit changes to your unfinished work. The solution to this issue is Git stash. Git stash takes your modified tracked files and saves them on a stack of unfinished changes that you can reapply at any time.
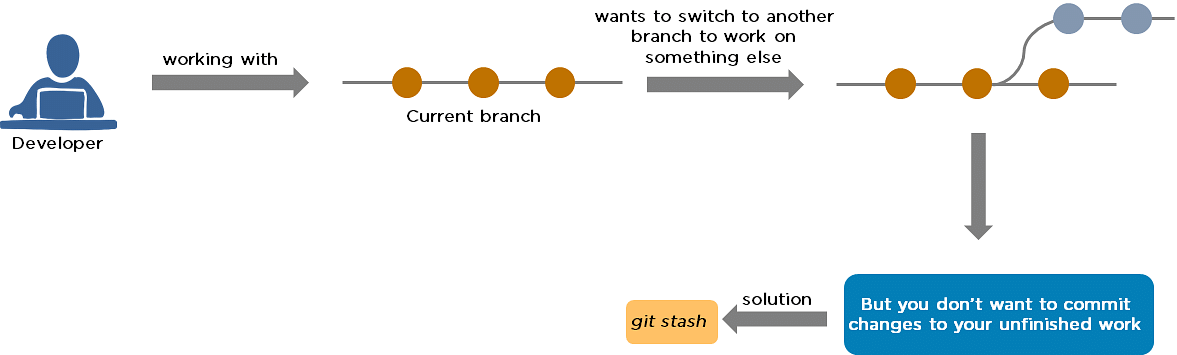
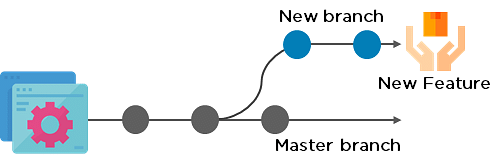
35. Explain the concept of branching in Git.
Suppose you are working on an application, and you want to add a new feature to the app. You can create a new branch and build the new feature on that branch.
- By default, you always work on the master branch
- The circles on the branch represent various commits made on the branch
- After you are done with all the changes, you can merge it with the master branch
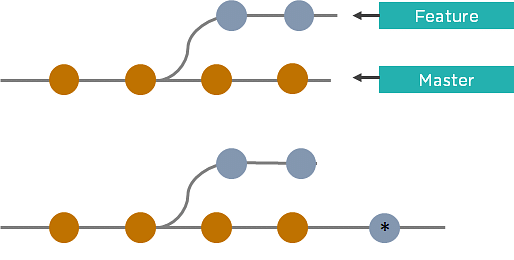
36. What is the difference between Git Merge and Git Rebase?
Suppose you are working on a new feature in a dedicated branch, and another team member updates the master branch with new commits. You can use these two functions:
Git Merge
To incorporate the new commits into your feature branch, use Git merge.
- Creates an extra merge commit every time you need to incorporate changes
- But, it pollutes your feature branch history
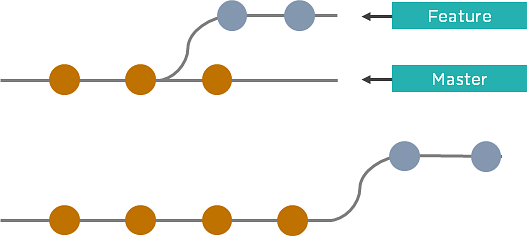
Git Rebase
As an alternative to merging, you can rebase the feature branch on to master.
- Incorporates all the new commits in the master branch
- It creates new commits for every commit in the original branch and rewrites project history
37. How do you find a list of files that have been changed in a particular commit?
The command to get a list of files that have been changed in a particular commit is:
git diff-tree –r {commit hash}
Example: git diff-tree –r 87e673f21b
- -r flag instructs the command to list individual files
- commit hash will list all the files that were changed or added in that commit
38. What is a merge conflict in Git, and how can it be resolved?
A Git merge conflict happens when you have merge branches with competing for commits, and Git needs your help to decide which changes to incorporate in the final merge.
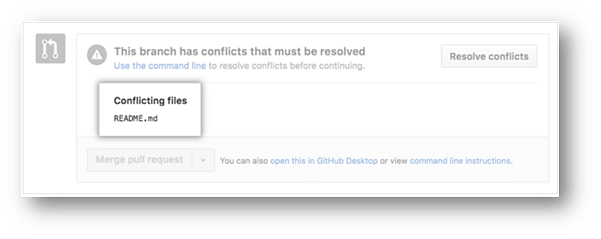
Manually edit the conflicted file to select the changes that you want to keep in the final merge.
Resolve using GitHub conflict editor
This is done when a merge conflict is caused after competing for line changes. For example, this may occur when people make different changes to the same line of the same file on different branches in your Git repository.
- Resolving a merge conflict using conflict editor:
- Under your repository name, click "Pull requests."
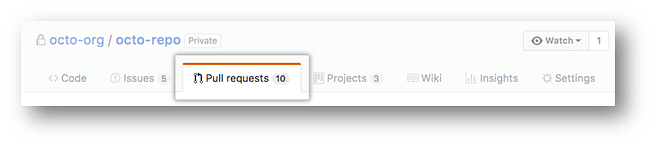
- In the "Pull requests" drop-down, click the pull request with a merge conflict that you'd like to resolve
- Near the bottom of your pull request, click "Resolve conflicts."
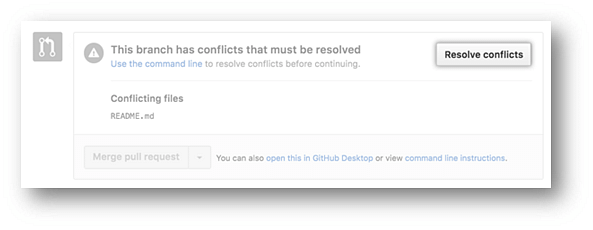
- Decide if you only want to keep your branch's changes, the other branch's changes, or make a brand new change, which may incorporate changes from both branches.
- Delete the conflict markers <<<<<<<, =======, >>>>>>> and make changes you want in the final merge.
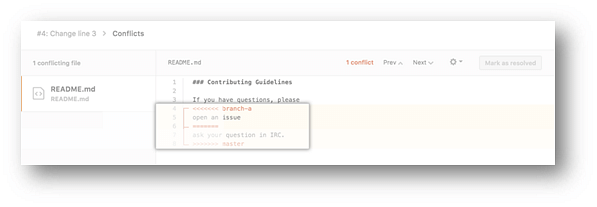
- If you have more than one merge conflict in your file, scroll down to the next set of conflict markers and repeat steps four and five to resolve your merge conflict.
- Once you have resolved all the conflicts in the file, click Mark as resolved.
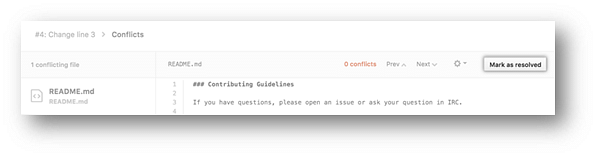
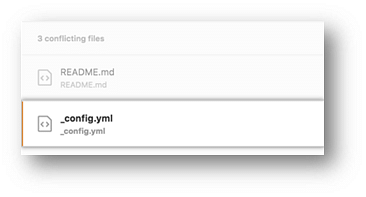
- If you have more than one file with a conflict, select the next file you want to edit on the left side of the page under "conflicting files" and repeat steps four to seven until you've resolved all of your pull request's merge conflicts.
- Once you've resolved your merge conflicts, click Commit merge. This merges the entire base branch into your head branch.

- To merge your pull request, click Merge pull request.
- A merge conflict is resolved using the command line.
- Open Git Bash.
- Navigate into the local Git repository that contains the merge conflict.

- Generate a list of the files that the merge conflict affects. In this example, the file styleguide.md has a merge conflict.

- Open any text editor, such as Sublime Text or Atom, and navigate to the file that has merge conflicts.
- To see the beginning of the merge conflict in your file, search the file for the conflict marker "<<<<<<<. " Open it, and you'll see the changes from the base branch after the line "<<<<<<< HEAD."
- Next, you'll see "=======", which divides your changes from the changes in the other branch, followed by ">>>>>>> BRANCH-NAME".

- Decide if you only want to keep your branch's changes, the other branch's changes, or make a brand new change, which may incorporate changes from both branches.
- Delete the conflict markers "<<<<<<<", "=======", ">>>>>>>" and make the changes you want in the final merge.
In this example, both the changes are incorporated into the final merge:

- Add or stage your changes.

- Commit your changes with a comment.
![]()
Now you can merge the branches on the command line, or push your changes to your remote repository on GitHub and merge your changes in a pull request.
39. What is Git bisect? How can you use it to determine the source of a (regression) bug?
Git bisect is a tool that uses binary search to locate the commit that triggered a bug.
Git bisect command -
git bisect <subcommand> <options>
The git bisect command is used in finding the bug performing a commit in the project by using a binary search algorithm.
The bug-occurring commit is called the “bad” commit, and the commit before the bug occurs is called the “good” commit. We convey the same to the git bisect tool, and it picks a random commit between the two endpoints and prompts whether that one is the “good” or “bad” one. The process continues until the range is narrowed down and the exact commit that introduced the exact change is discovered.
40. Explain some basic Git commands.
Some of the Basic Git Commands are summarized in the below table -
Command |
Purpose |
|
git init |
Used to start a new repository. |
|
git config:
|
This helps to set the username and email to whom the commits belong to. |
|
git clone <repository path> |
Used to create a local copy of an existing repository. |
|
git add:
|
Used to add one or more files to the staging area. |
|
git commit:
|
Creates a snapshot or records of the file(s) that are in the staging area. |
|
git diff:
|
Used to show differences between the two mentioned branches/differences made in the files in the staging area vs current version. |
|
git status |
Lists out all the files that are to be committed. |
|
git rm <file name(s)> |
Used to delete a file(s) from the current working directory and also stages it. |
|
git show <commit> |
Shows the content changes and metadata of the mentioned commit. |
|
git branch:
|
The first one creates a brand new branch. The second is used to delete the mentioned branch. The last one lists out all the branches available and also highlights the branch we are in currently. |
DevOps Interview Questions for Continuous Integration: Jenkins
41. Explain the master-slave architecture of Jenkins.

- Jenkins master pulls the code from the remote GitHub repository every time there is a code commit.
- It distributes the workload to all the Jenkins slaves.
- On request from the Jenkins master, the slaves carry out, builds, test, and produce test reports.
42. What is Jenkinsfile?
Jenkinsfile contains the definition of a Jenkins pipeline and is checked into the source control repository. It is a text file.
- It allows code review and iteration on the pipeline.
- It permits an audit trail for the pipeline.
- There is a single source of truth for the pipeline, which can be viewed and edited.
43. Which of the following commands runs Jenkins from the command line?
- java –jar Jenkins.war
- java –war Jenkins.jar
- java –jar Jenkins.jar
- java –war Jenkins.war
The correct answer is A) java –jar Jenkins.war
44. What concepts are key aspects of the Jenkins pipeline?
- Pipeline: User-defined model of a CD pipeline. The pipeline's code defines the entire build process, which includes building, testing, and delivering an application
- Node: A machine that is part of the Jenkins environment and capable of executing a pipeline
- Step: A single task that tells Jenkins what to do at a particular point in time
- Stage: Defines a conceptually distinct subset of tasks performed through the entire pipeline (build, test, deploy stages)
45. Which file is used to define dependency in Maven?
- build.xml
- pom.xml
- dependency.xml
- Version.xml
The correct answer is B) pom.xml
46. Explain the two types of pipelines in Jenkins, along with their syntax.
Jenkins provides two ways of developing a pipeline code: Scripted and Declarative.
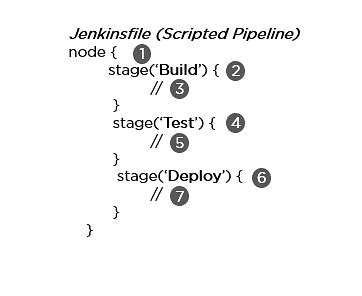
- Scripted Pipeline: It is based on Groovy script as their Domain Specific Language. One or more node blocks do the core work throughout the entire pipeline.
Syntax:
- Executes the pipeline or any of its stages on any available agent
- Defines the build stage
- Performs steps related to building stage
- Defines the test stage
- Performs steps related to the test stage
- Defines the deploy stage
- Performs steps related to the deploy stage
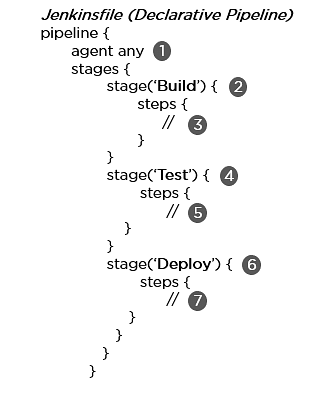
- Declarative Pipeline: It provides a simple and friendly syntax to define a pipeline. Here, the pipeline block defines the work done throughout the pipeline.
Syntax:
- Executes the pipeline or any of its stages on any available agent
- Defines the build stage
- Performs steps related to building stage
- Defines the test stage
- Performs steps related to the test stage
- Defines the deploy stage
- Performs steps related to the deploy stage
47. How do you create a backup and copy files in Jenkins?
In order to create a backup file, periodically back up your JENKINS_HOME directory.
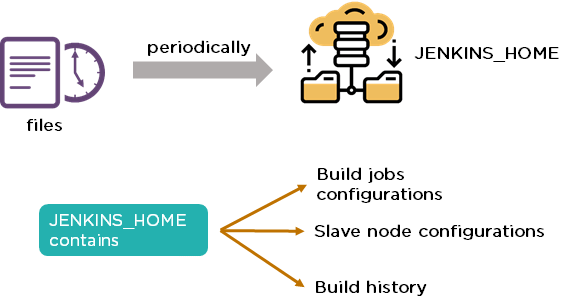
In order to create a backup of Jenkins setup, copy the JENKINS_HOME directory. You can also copy a job directory to clone or replicate a job or rename the directory.
48. How can you copy Jenkins from one server to another?
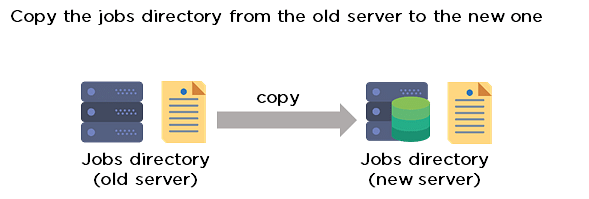
- Move the job from one Jenkins installation to another by copying the corresponding job directory.
- Create a copy of an existing job by making a clone of a job directory with a different name.
- Rename an existing job by renaming a directory.
49. Name three security mechanisms Jenkins uses to authenticate users.
- Jenkins uses an internal database to store user data and credentials.
- Jenkins can use the Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP) server to authenticate users.
- Jenkins can be configured to employ the authentication mechanism that the deployed application server uses.
50. How is a custom build of a core plugin deployed?
Steps to deploy a custom build of a core plugin:
- Copy the .hpi file to $JENKINS_HOME/plugins
- Remove the plugin's development directory
- Create an empty file called <plugin>.hpi.pinned
- Restart Jenkins and use your custom build of a core plugin
51. How can you temporarily turn off Jenkins security if the administrative users have locked themselves out of the admin console?

- When security is enabled, the Config file contains an XML element named useSecurity that will be set to true.
- By changing this setting to false, security will be disabled the next time Jenkins is restarted.
52. What are the ways in which a build can be scheduled/run in Jenkins?
- By source code management commits.
- After the completion of other builds.
- Scheduled to run at a specified time.
- Manual build requests.
53. What are the commands that you can use to restart Jenkins manually?
Two ways to manually restart Jenkins:
- (Jenkins_url)/restart // Forces a restart without waiting for builds to complete
- (Jenkins_url)/safeRestart // Allows all running builds to complete before it restarts
54. Explain how you can set up a Jenkins job?
To create a Jenkins Job, we go to the top page of Jenkins, choose the New Job option and then select Build a free-style software project.
The elements of this freestyle job are:
- Optional triggers for controlling when Jenkins builds.
- Optional steps for gathering data from the build, like collecting javadoc, testing results and/or archiving artifacts.
- A build script (ant, maven, shell script, batch file, etc.) that actually does the work.
- Optional source code management system (SCM), like Subversion or CVS.
DevOps Interview Questions for Continuous Testing: Selenium
55. What are the different Selenium components?
Selenium has the following components:
Selenium Integrated Development Environment (IDE)
- It has a simple framework and should be used for prototyping.
- It has an easy-to-install Firefox plug-in.
Selenium Remote Control (RC)
- Testing framework for a developer to write code in any programming language (Java, PHP, Perl, C#, etc.).
Selenium WebDriver
- Applies a better approach to automate browser activities.
- It does not rely on JavaScript.
Selenium Grid
- Works with Selenium RC and runs tests on different nodes using browsers.
56. What are the different exceptions in Selenium WebDriver?
Exceptions are events that occur during the execution of a program and disrupt the normal flow of a program's instructions. Selenium has the following exceptions:
- TimeoutException: It is thrown when a command performing an operation does not complete in the stipulated time.
- NoSuchElementException: It is thrown when an element with specific attributes is not found on the web page.
- ElementNotVisibleException: It is thrown when an element is present in Document Object Model (DOM) but is not visible. Ex: Hidden Elements defined in HTML using type=“hidden”.
- SessionNotFoundException: The WebDriver is performing the action immediately after quitting the browser.
57. Can Selenium test an application on an Android browser?
Selenium is capable of testing an application on an Android browser using an Android driver. You can use the Selendroid or Appium framework to test native apps or web apps in the Android browser. The following is a sample code:

58. What are the different test types that Selenium supports?
Functional: This is a type of black-box testing in which the test cases are based on the software specification.
Regression: This testing helps to find new errors, regressions, etc. in different functional and non-functional areas of code after the alteration.
Load Testing: This testing seeks to monitor the response of a device after putting a load on it. It is carried out to study the behavior of the system under certain conditions.
59. How can you access the text of a web element?
Get command is used to retrieve the text of a specified web element. The command does not return any parameter but returns a string value.
Used for:
- Verification of messages
- Labels
- Errors displayed on the web page
Syntax:
String Text=driver.findElement(By.id(“text”)).getText();
60. How can you handle keyboard and mouse actions using Selenium?
You can handle keyboard and mouse events with the advanced user interaction API. The advanced user interactions API contains actions and action classes.
Method |
Description |
| clickAndHold() | Clicks without releasing the current mouse location |
| dragAndDrop() | Performs click-and-hold at the location of the source element |
| keyDown(modifier_key) | Performs a modifier key press (ctrl, shift, Fn, etc.) |
| keyUp(modifier_key) | Performs a key release |
60. Which of these options is not a WebElement method?
- getText()
- size()
- getTagName()
- sendKeys()
The correct answer is B) size()
61. When do we use findElement() and findElements()?
- findElement()
It finds the first element in the current web page that matches the specified locator value.
Syntax:
WebElement element=driver.findElements(By.xpath(“//div[@id=‘example’]//ul//li”));
- findElements()
It finds all the elements in the current web page that matches the specified locator value.
Syntax:
List elementList=driver.findElements(By.xpath(“//div[@id=‘example’]//ul//li”));
62. What are driver.close() and driver.quit() in WebDriver?
These are two different methods used to close the browser session in Selenium WebDriver:
- driver.close(): This is used to close the current browser window on which the focus is set. In this case, there is only one browser open.
- driver.quit(): It closes all the browser windows and ends the WebDriver session using the driver.dispose method.
63. How can you submit a form using Selenium?
The following lines of code will let you submit a form using Selenium:
WebElement el = driver.findElement(By.id(“ElementID”));
el.submit();
64. What are the Testing types supported by Selenium?
There are two types of testing that are primarily supported by Selenium:
Functional Testing: Individual testing of software functional points or features.
Regression Testing: Wherever a bug is fixed, a product is retested and this is called Regression Testing.
65. What is Selenium IDE?
Selenium integrated development environment (IDE) is an all-in-one Selenium script development environment. It may be used to debug tests, alter and record and is also available as a Firefox extension. Selenium IDE comes with the whole Selenium Core that allows us to rapidly and easily replay and record tests in the exact environment where they will be conducted.
Selenium IDE is the best environment for building Selenium tests, regardless of the style of testing we prefer, thanks to the ability to move instructions around rapidly and the autocomplete support.
66. What is the difference between Assert and Verify commands in Selenium?
The difference between Verify and Assert commands in Selenium are:
- The verify commands determine whether or not the provided condition is true. The program execution does not halt regardless of whether the condition is true or not, i.e., all test steps will be completed, and verification failure will not stop the execution.
- The assert command determines whether a condition is false or true. To know whether the supplied element is on the page or not, we do the following. The next test step will be performed by the program control, if the condition is true. However, no further tests will be run, and the execution will halt, if the condition is false.
67. How to launch Browser using WebDriver?
To launch Browser using WebDriver, following syntax is followed -
WebDriver driver = new InternetExplorerDriver();
WebDriver driver = new ChromeDriver();
WebDriver driver = new FirefoxDriver();
68. What is the difference between Asset Management and Configuration Management?
Differences between Configuration Management and Asset Management are:
Configuration Management |
Asset Management |
|
Operational Relationships. |
Incidental relationships only. |
|
Maintains troubleshooting data. |
Maintains taxes data. |
|
Everything we deploy is scope. |
Everything we own is scope. |
|
Deployment to retirement - lifecycle. |
Purchase to disposal - lifecycle. |
|
Operations - main concern. |
Finances - main concern. |
|
ITIL processes from interfacing. |
Leasing and purchasing from interfacing. |
DevOps Interview Questions for Configuration Management: Chef, Puppet, Ansible
69. Why are SSL certificates used in Chef?
- SSL certificates are used between the Chef server and the client to ensure that each node has access to the right data.
- Every node has a private and public key pair. The public key is stored at the Chef server.
- When an SSL certificate is sent to the server, it will contain the private key of the node.
- The server compares this against the public key in order to identify the node and give the node access to the required data.

70. Which of the following commands would you use to stop or disable the 'httpd' service when the system boots?
- # systemctl disable httpd.service
- # system disable httpd.service
- # system disable httpd
- # systemctl disable httpd.service
The correct answer is A) # systemctl disable httpd.service
71. What is Test Kitchen in Chef?
Test Kitchen is a command-line tool in Chef that spins up an instance and tests the cookbook on it before deploying it on the actual nodes.
Here are the most commonly used kitchen commands:

72. How does chef-apply differ from chef-client?
- chef-apply is run on the client system.
chef-apply applies the recipe mentioned in the command on the client system.
$ chef-apply recipe_name.rb
- chef-client is also run on the client system.
chef-client applies all the cookbooks in your server's run list to the client system.
$ knife chef-client
73. What is the command to sign the requested certificates?
- For Puppet version 2.7:
# puppetca –sign hostname-of-agent
Example:
# puppetca –sign ChefAgent
# puppetca sign hostname-of-agent
Example:
# puppetca sign ChefAgent
- For Puppet version 2.7:
# puppetca –sign hostname-of-agent
Example:
# puppetca –sign ChefAgent
# puppetca sign hostname-of-agent
Example:
# puppetca sign ChefAgent
74. Which open-source or community tools do you use to make Puppet more powerful?
- Changes in the configuration are tracked using Jira, and further maintenance is done through internal procedures.
- Version control takes the support of Git and Puppet's code manager app.
- The changes are also passed through Jenkin's continuous integration pipeline.
75. What are the resources in Puppet?
- Resources are the basic units of any configuration management tool.
- These are the features of a node, like its software packages or services.
- A resource declaration, written in a catalog, describes the action to be performed on or with the resource.
- When the catalog is executed, it sets the node to the desired state.
76. What is a class in Puppet?
Classes are named blocks in your manifest that configure various functionalities of the node, such as services, files, and packages.
The classes are added to a node's catalog and are executed only when explicitly invoked.
Class apache (String $version = ‘latest’) {
package{
‘httpd’: ensure => $version,
before => File[‘/etc/httpd.conf’],}
77. What is an Ansible role?
An Ansible role is an independent block of tasks, variables, files, and templates embedded inside a playbook.
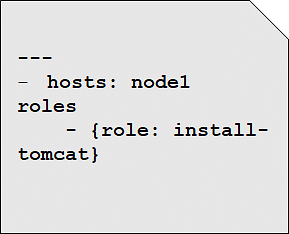
This playbook installs tomcat on node1.
78. When should I use '{{ }}'?
Always use {{}} for variables, unless you have a conditional statement, such as "when: …". This is because conditional statements are run through Jinja, which resolves the expressions.
For example:
echo “This prints the value of {{foo}}”
when : foo is defined
Using brackets makes it simpler to distinguish between strings and undefined variables.

This also ensures that Ansible doesn't recognize the line as a dictionary declaration.
79. What is the best way to make content reusable/redistributable?
There are three ways to make content reusable or redistributable in Ansible:
- Roles are used to managing tasks in a playbook. They can be easily shared via Ansible Galaxy.
- "include" is used to add a submodule or another file to a playbook. This means a code written once can be added to multiple playbooks.
- "import" is an improvement of "include," which ensures that a file is added only once. This is helpful when a line is run recursively.
80. How is Ansible different from Puppet?
Ansible |
Puppet |
| Easy agentless installation | Agent-based installation |
| Based on Python | Based on Ruby |
| Configuration files are written in YAML | Configuration files are written in DSL |
| No support for Windows | Support for all popular OS's |
We will now look at some DevOps interview questions on contanerization.
DevOps Interview Questions on Containerization
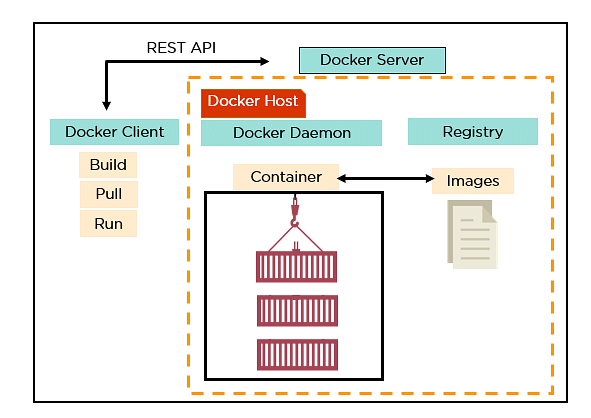
81. Explain the architecture of Docker.
- Docker uses a client-server architecture.
- Docker Client is a service that runs a command. The command is translated using the REST API and is sent to the Docker Daemon (server).
- Docker Daemon accepts the request and interacts with the operating system to build Docker images and run Docker containers.
- A Docker image is a template of instructions, which is used to create containers.
- Docker container is an executable package of an application and its dependencies together.
- Docker registry is a service to host and distribute Docker images among users.
82. What are the advantages of Docker over virtual machines?
Criteria |
Virtual Machine |
Docker |
| Memory space | Occupies a lot of memory space | Docker containers occupy less space |
| Boot-up time | Long boot-up time | Short boot-up time |
| Performance | Running multiple virtual machines leads to unstable performance | Containers have a better performance, as they are hosted in a single Docker engine |
| Scaling | Difficult to scale up | Easy to scale up |
| Efficiency | Low efficiency | High efficiency |
| Portability | Compatibility issues while porting across different platforms | Easily portable across different platforms |
| Space allocation | Data volumes cannot be shared | Data volumes are shared and used again across multiple containers |
83. How do we share Docker containers with different nodes?
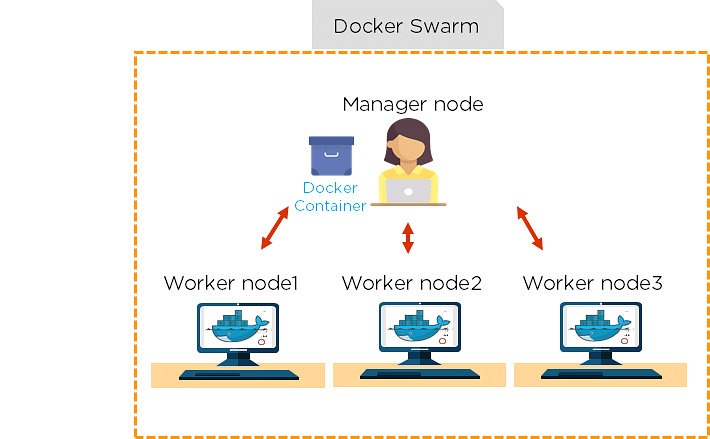
- It is possible to share Docker containers on different nodes with Docker Swarm.
- Docker Swarm is a tool that allows IT administrators and developers to create and manage a cluster of swarm nodes within the Docker platform.
- A swarm consists of two types of nodes: a manager node and a worker node.
84. What are the commands used to create a Docker swarm?
- Create a swarm where you want to run your manager node.
Docker swarm init --advertise-addr <MANAGER-IP>
- Once you've created a swarm on your manager node, you can add worker nodes to your swarm.
- When a node is initialized as a manager, it immediately creates a token. In order to create a worker node, the following command (token) should be executed on the host machine of a worker node.
docker swarm join \ --token SWMTKN-1-49nj1cmql0jkz5s954yi3oex3nedyz0fb0xx14ie39trti4wxv-8vxv8rssmk743ojnwacrr2e7c \ 192.168.99.100:2377
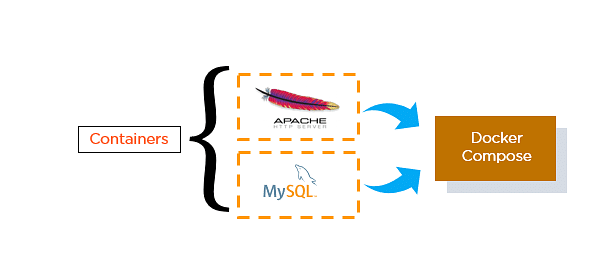
85. How do you run multiple containers using a single service?
- It is possible to run multiple containers as a single service with Docker Compose.
- Here, each container runs in isolation but can interact with each other.
- All Docker Compose files are YAML files.
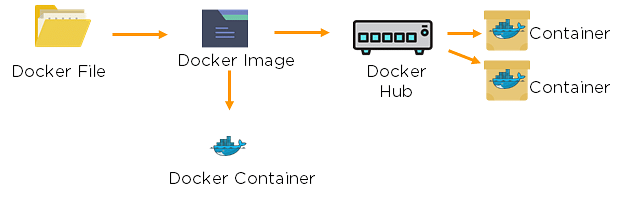
86. What is a Dockerfile used for?
- A Dockerfile is used for creating Docker images using the build command.
- With a Docker image, any user can run the code to create Docker containers.
- Once a Docker image is built, it's uploaded in a Docker registry.
- From the Docker registry, users can get the Docker image and build new containers whenever they want.
87. Explain the differences between Docker images and Docker containers.
Docker Images |
Docker Container |
| Docker images are templates of Docker containers | Containers are runtime instances of a Docker image |
| An image is built using a Dockerfile | Containers are created using Docker images |
| It is stored in a Docker repository or a Docker hub | They are stored in the Docker daemon |
| The image layer is a read-only filesystem | Every container layer is a read-write filesystem |
88. Instead of YAML, what can you use as an alternate file for building Docker compose?
To build a Docker compose, a user can use a JSON file instead of YAML. In case a user wants to use a JSON file, he/she should specify the filename as given:
Docker-compose -f Docker-compose.json up
89. How do you create a Docker container?
Task: Create a MySQL Docker container
A user can either build a Docker image or pull an existing Docker image (like MySQL) from Docker Hub.
Now, Docker creates a new container MySQL from the existing Docker image. Simultaneously, the container layer of the read-write filesystem is also created on top of the image layer.
- Command to create a Docker container: Docker run -t –i MySQL
- Command to list down the running containers: Docker ps
90. What is the difference between a registry and a repository?
Registry |
Repository |
| A Docker registry is an open-source server-side service used for hosting and distributing Docker images | The repository is a collection of multiple versions of Docker images |
| In a registry, a user can distinguish between Docker images with their tag names | It is stored in a Docker registry |
| Docker also has its own default registry called Docker Hub | It has two types: public and private repositories |
91. What are the cloud platforms that support Docker?
The following are the cloud platforms that Docker runs on:
- Amazon Web Services
- Microsoft Azure
- Google Cloud Platform
- Rackspace

92. What is the purpose of the expose and publish commands in Docker?
Expose
- Expose is an instruction used in Dockerfile.
- It is used to expose ports within a Docker network.
- It is a documenting instruction used at the time of building an image and running a container.
- Expose is the command used in Docker.
- Example: Expose 8080
Publish
- Publish is used in a Docker run command.
- It can be used outside a Docker environment.
- It is used to map a host port to a running container port.
- --publish or –p is the command used in Docker.
- Example: docker run –d –p 0.0.0.80:80
Now, let's have a look at the DevOps interview questions for continuous monitoring.
DevOps Interview Questions for Continuous Monitoring
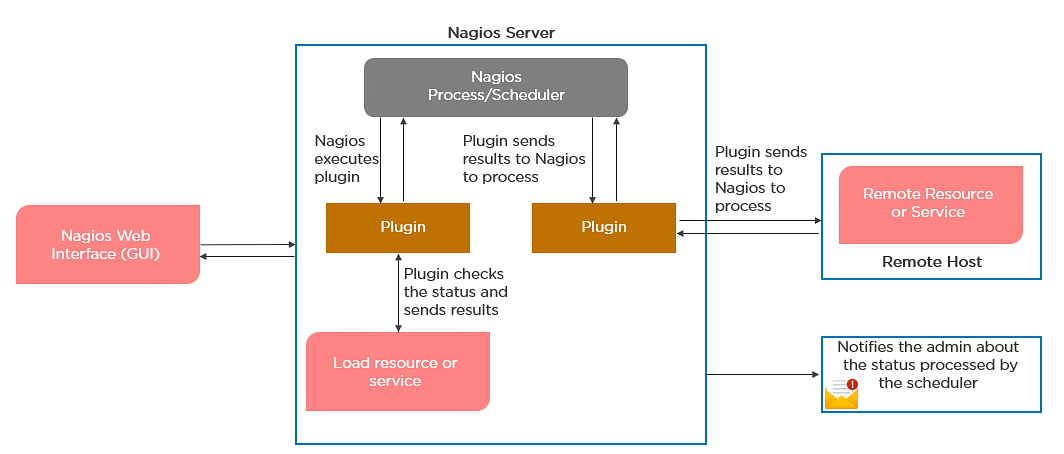
93. How does Nagios help in the continuous monitoring of systems, applications, and services?
Nagios enables server monitoring and the ability to check if they are sufficiently utilized or if any task failures need to be addressed.
- Verifies the status of the servers and services
- Inspects the health of your infrastructure
- Checks if applications are working correctly and web servers are reachable
94. How does Nagios help in the continuous monitoring of systems, applications, and services?
95. What do you mean by Nagios Remote Plugin Executor (NPRE) of Nagios?
Nagios Remote Plugin Executor (NPRE) enables you to execute Nagios plugins on Linux/Unix machines. You can monitor remote machine metrics (disk usage, CPU load, etc.)
- The check_npre plugin that resides on the local monitoring machine
- The NPRE daemon that runs on the remote Linux/Unix machine
96. What are the port numbers that Nagios uses for monitoring purposes?
Usually, Nagios uses the following port numbers for monitoring:

97. What are active and passive checks in Nagios?
Nagios is capable of monitoring hosts and services in two ways:
Actively
- Active checks are initiated as a result of the Nagios process
- Active checks are regularly scheduled
Passively
- Passive checks are initiated and performed through external applications/processes
- Passive checks results are submitted to Nagios for processing
98. What are active and passive checks in Nagios?
Active Checks:
- The check logic in the Nagios daemon initiates active checks.
- Nagios will execute a plugin and pass the information on what needs to be checked.
- The plugin will then check the operational state of the host or service, and report results back to the Nagios daemon.
- It will process the results of the host or service check and send notifications.
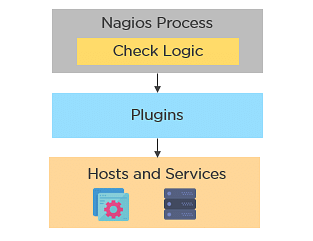
Passive Checks:
- In passive checks, an external application checks the status of a host or service.
- It writes the results of the check to the external command file.
- Nagios reads the external command file and places the results of all passive checks into a queue for later processing.
- Nagios may send out notifications, log alerts, etc. depending on the check result information.

99. Explain the main configuration file and its location in Nagios.
The main configuration file consists of several directives that affect how Nagios operates. The Nagios process and the CGIs read the config file.
A sample main configuration file will be placed into your settings directory:
/usr/local/Nagios/etc/resource.cfg
100. What is the Nagios Network Analyzer?
- It provides an in-depth look at all network traffic sources and security threats.
- It provides a central view of your network traffic and bandwidth data.
- It allows system admins to gather high-level information on the health of the network.
- It enables you to be proactive in resolving outages, abnormal behavior, and threats before they affect critical business processes.
101. What are the benefits of HTTP and SSL certificate monitoring with Nagios?
HTTP Certificate Monitoring
- Increased server, services, and application availability.
- Fast detection of network outages and protocol failures.
- Enables web transaction and web server performance monitoring.
SSL Certificate Monitoring
- Increased website availability.
- Frequent application availability.
- It provides increased security.
102. Explain virtualization with Nagios.

Nagios can run on different virtualization platforms, like VMware, Microsoft Visual PC, Xen, Amazon EC2, etc.
- Provides the capability to monitor an assortment of metrics on different platforms
- Ensures quick detection of service and application failures
- Has the ability to monitor the following metrics:
- CPU Usage
- Memory
- Networking
- VM status
- Reduced administrative overhead
103. Name the three variables that affect recursion and inheritance in Nagios.
Name: Template name that can be referenced in other object definitions so it can inherit the object's properties/variables.
Use: Here, you specify the name of the template object that you
want to inherit properties/variables from.
register: This variable indicates whether or not the object definition
should be registered with Nagios.
define someobjecttype{
object-specific variables ….
name template_name
use name_of_template
register [0/1]
}
104. Why is Nagios said to be object-oriented?

Using the object configuration format, you can create object definitions that inherit properties from other object definitions. Hence, Nagios is known as object-oriented.
Types of Objects:
- Services
- Hosts
- Commands
- Time Periods
105. Explain what state stalking is in Nagios.
- State stalking is used for logging purposes in Nagios.
- When stalking is enabled for a particular host or service, Nagios will watch that host or service very carefully.
- It will log any changes it sees in the output of check results.
- This helps in the analysis of log files.
Version Control System Interview Questions
Here are some common interview questions and answers related to version control systems:
106. What is a version control system (VCS)?
A VCS is a software tool that allows developers to manage changes to the source code of a software project. It enables developers to track and manage different versions of code files, collaborate with others, and revert to earlier versions if necessary.
107. What are the benefits of using a VCS?
There are several benefits to using a VCS, including:
- The ability to track changes to code over time
- The ability to collaborate with other developers and share code
- The ability to revert to earlier versions of code if necessary
- The ability to branch code and work on different features or fixes simultaneously
- The ability to merge changes from other branches or contributors
- Increased confidence and control over code changes and deployments
108. What are the types of VCS?
There are two main types of VCS: centralized and distributed.
- Centralized VCS: A centralized VCS has a single central repository that stores all versions of the code files. Developers check out files from the central repository, make changes, and then commit the changes back to the warehouse.
- Distributed VCS: A distributed VCS allows developers to create their local repositories of code changes. Developers can work on code changes locally, commit changes to their local storage, and then push changes to a central repository or pull changes from other contributors.
109. What is the difference between Git and SVN?
Git and SVN are both popular VCS tools, but they have some key differences:
- Git is a distributed VCS, while SVN is a centralized VCS.
- Git is more flexible and allows easier branching and merging of code changes.
- SVN has better support for handling binary files.
- Git is generally considered faster than SVN.
Virtualization Interview Questions
110. What is virtualization?
Virtualization is a technology that allows multiple operating systems or applications to run on a single physical server or computer. It creates virtual instances of hardware resources such as CPU, memory, and storage, which can be allocated to different virtual machines.
111. What are the benefits of virtualization?
There are several benefits of virtualization, including:
- Reduced hardware costs
- Increased efficiency and utilization of resources
- Improved scalability and flexibility
- Increased reliability and availability of applications
- Simplified management and administration of IT infrastructure
112. What are the different types of virtualization?
There are several types of virtualization, including:
- Server virtualization: Running multiple operating systems on a single physical server.
- Network virtualization: Creating virtual networks that operate independently of physical network infrastructure.
- Storage virtualization: Combining physical storage resources into a single virtual storage pool.
- Desktop virtualization: Running multiple desktop environments on a single physical machine.
113. What is a hypervisor?
A hypervisor is a layer of software that enables virtualization by allowing multiple virtual machines to share a single physical server or computer. It manages the allocation of hardware resources to each virtual machine and isolates each virtual machine from the others.
Most Frequently Asked Questions
There are some frequently asked questions related to DevOps virtualization:
114. What is virtualization, and how does it connect to DevOps?
Virtualization is creating a virtual version of something, such as a server, storage device, or network. In DevOps, virtualization allows teams to create and manage virtual environments that can be used for development, testing, and deployment. This can help improve efficiency, reduce costs, and enable greater flexibility and scalability.
115. What are the benefits of using virtualization in DevOps?
Virtualization offers several benefits in a DevOps environment, including:
- Improved efficiency: Virtualization allows for faster creation, deployment, and management of development and testing environments.
- Greater scalability: Virtualization enables teams to quickly scale up or down their infrastructure as needed without requiring additional physical hardware.
- Increased flexibility: Virtualization allows the creation of custom environments that can be easily modified and adapted to meet changing requirements.
- Reduced costs: Virtualization can help reduce hardware costs and increase resource utilization, leading to lower overall infrastructure costs.
116. What are some standard virtualization technologies used in DevOps?
Several virtualization technologies are commonly used in DevOps, including:
- Virtual machines (VMs): VMs are created using virtualization software such as VMware or VirtualBox and enable the creation of multiple virtual instances of an operating system on a single physical machine.
- Containers: Containers are lightweight, portable virtual environments created using containerization software such as Docker or Kubernetes. Containers enable the creation of custom application environments that can be easily shared and deployed across different systems.
- Cloud computing: Cloud computing providers such as Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and the Google Cloud Platform (GCP) offer virtualized infrastructure and services that can be easily managed and scaled using DevOps tools and practices.
Next Steps
There you go, these are some of the most common DevOps interview questions that you might come across while attending an interview. As a DevOps Engineer, in-depth knowledge of processes, tools, and relevant technology is essential and these DevOps interview questions and answers will help you get some knowledge about some of these aspects. In addition, you must also have a holistic understanding of the products, services, and systems in place.
After completing our Post Graduate Program in DevOps, Chaance Graves was able to enhance his skill set and accelerate his career growth. Read his success story in our Simplilearn Post Graduate in DevOps Review here.
As you can see, there is a lot to learn to be able to land a rewarding job in the field of DevOps—Git, Jenkins, Selenium, Chef, Puppet, Ansible, Docker, Nagios, and more. While this comprehensive DevOps interview question guide is designed to help you ace your next interview, you would undoubtedly perform better if you enroll in our comprehensive DevOps Engineer Training Course today. You can even check out our Post Graduate Program in DevOps designed in collaboration with Caltech CTME that enables you to prepare for a DevOps career.
In the context of DevOps interview questions and answers, the AWS Solution Architect Certification often plays a significant role, highlighting a candidate's expertise in AWS cloud infrastructure, a key component of modern DevOps practices. This certification is frequently used during interviews to assess a candidate's ability to design, manage, and optimize cloud-based solutions.