Imagine buying a piece of digital artwork on the Internet at a reasonable price and getting a unique digital token known which proves your authority over the artwork you bought. Wouldn't it be great? Well, that opportunity exists now, thanks to NFTs.
NFTs are currently taking the digital art and collectables world by storm. Just as everyone worldwide believed Bitcoin was the digital answer to currency, NFTs are now pitched as the digital answer to collectibles. Asa result, digital artists are seeing their lives changing thanks to the massive sales to a new crypto audience.
If you are interested in NFTs and want to explore more about what they are, you have come to the right place. Let’s dive in and see what all the fuss is about!
What is NFT?
NFT means non-fungible tokens (NFTs), which are generally created using the same type of programming used for cryptocurrencies. In simple terms these cryptographic assets are based on blockchain technology. They cannot be exchanged or traded equivalently like other cryptographic assets.
Like Bitcoin or Ethereum. The term NFT clearly represents it can neither be replaced nor interchanged because it has unique properties. Physical currency and cryptocurrency are fungible, which means that they can be traded or exchanged for one another.
Immerse yourself in the revolutionary world of NFTs while building a robust foundation in cybersecurity through our dedicated cyber security bootcamp. Discover the intricacies of non-fungible tokens and their impact on digital ownership, all while honing your skills in protecting these valuable assets from cyber threats. With hands-on training in encryption, blockchain security, and risk mitigation, you'll be well-prepared to navigate the evolving landscape of NFTs with confidence. Join us to bridge the gap between cutting-edge technology and cybersecurity expertise in a single transformative program.

- NFT stands for a non-fungible token, which means it can neither be replaced nor interchanged because it has unique properties.
Key Features of NFT -
- Digital Asset - NFT is a digital asset that represents Internet collectibles like art, music, and games with an authentic certificate created by blockchain technology that underlies Cryptocurrency.
- Unique - It cannot be forged or otherwise manipulated.
- Exchange - NFT exchanges take place with cryptocurrencies such as Bitcoin on specialist sites.
Cryptopunks is a notable example of an NFT. It enables you to buy, sell and store 10,000 collectibles with proof-of-ownership.
History of Non-Fungible Tokens (NFTs)
As sometimes happens with innovative technology, NFTs did not just come out of the blue and become popular overnight. It leads to the question of when the first NFT came into existence.
According to some, Colored Coins, which was initiated in 2012, has the honor of being the first NFT. In the words of investor Andrew Steinworld, he said that one might argue that the Colored Coins were the NFT that first came into existence. Colored Coins exhibited a major leap in the capabilities of Bitcoin, however, they had a downside too. They could represent only some values if their worth is agreed upon by everyone. The scripting language of Bitcoin did not enable this type of behavior within the network it is in.
Some argue that “Quantum” NFT by Kevin McCoy minted on the Namecoin Blockchain on 2nd May 2014 is the first rightful owner of an NFT title. A project called “CryptoKitties” by Dapper Labs on Ethereum was the implementation of NFTs widely recognized as the first of its kind. When the 2017 crypto boom happened, those digital cats were priced at 600 Eth (or USD 172k) and mainstream attention was drawn globally. Since then, ample NFT projects have come up with a huge amount of success.
What is Blockchain?
Blockchain refers to a method of documenting data that ensures its security and integrity. This makes it impossible or difficult to modify, cheat or hack the system. A blockchain is essentially a digital documentation of transactions that is disseminated and replicated across a network or computer systems that uses blockchain technology
Blockchain and Fungibility
These are two concepts that can be related closely but also can pose some difficulties when combined. Fungibility pertains to a commodity or asset’s ability to be exchanged easily for another similar unit without any difference in quality or value. Blockchain technology, however, creates a transparent and immutable record of transactions and ownership.
For instance, if a certain cryptocurrency is involved in an unlawful activity, it may be told to be non-fungible or tainted, which means that it cannot be used interchangeably with other units of the same cryptocurrency. This leads to a loss of liquidity or value for the asset that is affected. However, a lot of solutions are currently being developed, like mixing privacy or services-focused cryptocurrency, to address this problem and to ensure fungibility while preserving the security and fungibility of blockchain technology.
How Does NFT Work?
Now that you've taken your initial steps in understanding what an NFT is, you should continue on and learn about how an NFT works.
- The majority of NFTs reside on the Ethereum cryptocurrency's blockchain, a distributed public ledger that records transactions.
- NFTs are individual tokens with valuable information stored in them.
- Because they hold a value primarily set by the market and demand, they can be bought and sold just like other physical types of art.
- NFTs' unique data makes it easy to verify and validate their ownership and the transfer of tokens between owners.
Examples of NFT
The NFT world is relatively new to people. Here are some examples of NFTs that exist today:
- A Digital Collectible
- Domain Names
- Games
- Essays
- Sneakers in fashion line
What is NFT Used For?
People interested in Crypto-trading and people who like to collect artwork often use NFTs. Other than that, it has some other uses too like:
- Digital Content - The most significant use of NFTs today is in digital content. Content creators see their profits enhanced by NFTs, as they power a creator economy where creators have the ownership of their content over to the platforms they use to publicize it.

- Gaming Items - NFTs have garnered considerable interest from game developers. NFTs can provide a lot of benefits to the players. Normally, in an online game, you can buy items for your character, but that’s as far as it goes. With NFTs, you can recoup your money by selling the items once you’re finished with them.
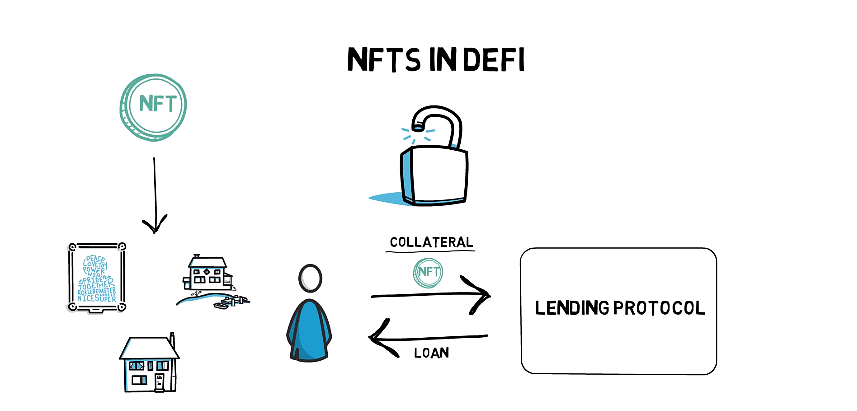
- Investment and Collaterals - Both NFT and DeFi (Decentralized Finance) share the same infrastructure. DeFi applications let you borrow money by using collateral. NFT and DeFi both work together to explore using NFTs as collateral instead.
- Domain Names - NFTs provide your domain with an easier-to-remember name. This works like a website domain name, making its IP address more memorable and valuable, usually based on length and relevance.

Even celebrities like Snoop Dogg, Shawn Mendes, and Jack Dorsey are taking an interest in the NFT by releasing unique memories and artwork and selling them as securitized NFTs.
NBA Top Shot Is a Hot NFT Use Case
One of the most popular non-fungible tokens in recent days is NBA Top Shot, a partnership between Dapper Labs (makers of the CryptoKitties game) and the National Basketball Association (NBA). The NBA licenses individual highlight video reels, among other content, to Dapper Labs, and they digitize the footage and make it available for sale to consumers. Each reel shows a video clip, such as a famous player's basketball dunk, some featuring different angles and digital artwork to make them unique. Even if someone made a perfect copy of the video, it can be instantly recognizable as a counterfeit. The venture has already generated $230 million in sales, and the company just also received $305 million in funding from a group that includes Michael Jordan and Kevin Durant.
These video reels are selling at high prices. Among the most popular:
- LeBron James “Cosmic” Dunk: $208,000
- Zion Williamson “Holo MMXX” Block: $100,000
- LeBron James “From the Top” Block: $100,000
- LeBron James “Throwdowns” Dunk: $100,000
- LeBron James “Holo MMXX” Dunk: $99,999
- Steph Curry “Deck the Hoops” Handles: $85,000
- Giannis Antetokounmpo “Holo MMXX” Dunk: $85,000
- LeBron James “From the Top” Dunk: $80,000
These unique NBA moments are minted and released into the marketplace via “pack drops.” The most common sell for only nine dollars, but more exclusive packs can sell for much more.
Now that you’ve understood what is NFT used for, and the various ways you can benefit from it, let’s take a look at how it is specifically different from other forms on cryptocurrency.
NFTs vs. Crypto and Fiat currencies. What's the Difference?
NFTs or Non-Fungible Tokens are a kind of cryptocurrency that represents a one-of-a-kind digital asset or unique piece of artwork. Fiat and cryptocurrencies are mainly used for transactional purposes and are fungible, which means each unit can be interchanged. Being created on blockchain technology, NFTs allow the transfer of ownership and transparent ownership. They allow artists to monetize their creations made digitally and thus have gained huge popularity. Crypto and fiat currencies, on the other hand, are used mainly as a store of value or medium of exchange. While there are certain similarities, the unique features of NFTs make them different from traditional currencies.
What is an NFT Marketplace?
It is a marketplace that is a public Blockchain platform. Though it is in its early stages, this marketplace is gaining popularity and inspiring businesses and developers to construct a marketplace.
Benefits of Non-Fungible Tokens
There are several advantages of NFTs, some of these include:
- NFTs can be invested in by anyone as it is accessible to all and sundry. An NFT can be more efficiently and easily transferred among people around the globe.
- A blockchain secures NFT ownership. The digital signature of ownership can make the ownership of an investor quite secure. The ownership also gets transparent due to the blockchain technology.
- NFTs provide the scope for learning more about blockchain technology. The investors can do so while making their portfolios diverse and allocating a small amount of tokenized assets.
Why Are NFTs Becoming Popular?
NFTs have actually been around since 2015, but they are now experiencing a boost in popularity thanks to several factors. First, and perhaps most obviously, is the normalization and excitement of cryptocurrencies and the underlying blockchain frameworks. Beyond the technology itself is the combination of fandom, the economics of royalties, and the laws of scarcity. Consumers all want to get in on the opportunity to own unique digital content and potentially hold them as a type of investment.
When someone buys a non-fungible token, they gain ownership of the content, but it can still make its way over the Internet. In this way, an NFT can gain popularity — the more it’s seen online, the more value it develops. When the asset is sold, the original creator gets a 10 percent cut, with the platform getting a small percentage and the current owner getting the rest of that revenue. Thus, there is potential for ongoing revenue from popular digital assets as they are bought and sold over time.
Authenticity is the name of the game with NFTs. Digital collectibles contain distinguishing information that make them distinct from any other NFT and easily verifiable, thanks to the blockchain. Creating and circulating fake collectibles doesn’t work because each item can be traced back to the original creator or issuer. And, unlike cryptocurrencies, they can’t be directly exchanged with one another (like baseball cards in real life) because no two are the same.
Are NFTs Mainstream Now?
So, with all the fuss made over NFTs, is it accurate to say that they’re now mainstream? This article makes a strong case for believing that NFTs are now baked into the public consciousness. It doesn’t hurt that a number of high-profile celebrities have ventured into NFT waters.
While perhaps it may be premature to say “Yes, NFTs are definitely mainstream now,” if they continue on this trajectory, 2022 could be the year where we know that NFTs are here to stay.
What’s Worth Picking Up at the NFT Supermarket?
One can consider a variety of unique digital assets based on personal preferences and interests at the NFT supermarket. Digital art is a popular category that includes unique pieces made by upcoming and well-known creators. Collectibles can be picked up too. These range from one-of-a-kind in-game items to virtual trading cards. Recent times have also seen sports-related NFTs like game highlights or limited edition player cards gain popularity. One can also explore virtual gaming and real estate assets that allow the buyers to trade and own game items or digital land. It is of utmost importance to conduct research on the value and authenticity of an NFT before purchasing it. This is due to the fact that the market is still evolving and is subject to volatility.
Properties of NFT
- NFTs cannot be divided into smaller parts while retaining their inherent qualities. This distinguishes them from fungible tokens like a pound note, which can be subdivided into pence.
- When an entity mints NFT, it can sell to a new entity that can become the owner of that NFT. But, depending on a specific set of circumstances, smart contract rules may be utilized to restrict or stop further token transfers.
- Though an NFT has specific properties when it is created, those properties can be updated over time through smart contracts when certain conditions are met; this is akin to a ‘pass the parcel’ game where a parcel loses a layer of wrapping every time the music pauses.
Applications of NFT
NFTs applications can be found in several industries, such as gaming, art, sports and music. The creators of the art world are enabled to monetize their art created digitally and provide a unique record of ownership for collectors that is verifiable. In the same way, NFTs can be used to trade and create virtual assets in the gaming industry, including virtual real estate and in-game items. NFTs can be beneficial to the music industry by creating one-of-a-kind digital collectibles, while in sports, they can offer fan experiences and limited-edition memorabilia. Besides these, NFTs can also be used to verify and authenticate the ownership of physical assets like real estate and luxury goods.
How is an NFT Different From Other Cryptocurrencies?
Although NFTs are created using the same kind of programming language as other cryptocurrencies, that's where the similarity ends.
Other Cryptocurrency |
NFT |
|
|
Also Read: Bitcoin vs Ethereum: Which One is Better?
Ethereum and NFTs

Ethereum blockchain makes it possible for NFTs to work for several reasons:
- Trading NFTs, without needing peer-to-peer platforms, can take significant cuts as compensation.
- All Ethereum products share the same "backend", making NFTs portable to buy on one product and sell it on another effortlessly.
- Once a transaction is confirmed, it's impossible to manipulate the data to forge the ownership.
- Ethereum never goes down, which means your tokens will always be available to sell.
Penguin Communities
Pudgy Penguin is a popular non-fungible token community, a cryptocurrency subcategory representing ownership in a unique asset: 8,888 penguins on the Ethereum blockchain, organized into one collection. Pudgy Penguin is just one of many communities out there that offer benefits and other advantages to members, such as having a membership on a shared Discord server or gaining access to a private Telegram channel that lets you talk with other owners.
Many NFT projects have their own communities, where members can collaborate, share ideas, and support or buy each other’s projects or art.
How to Buy NFTs?
Having understood what NFTs are used for and its specific advantages over other cryptocurrencies, you might want to venture into buying NFTs. If so, you will need to acquire some essential items before you do it:
- You’ll need a digital wallet that allows you to store your NFTs and cryptocurrencies.
- Then you need to purchase some cryptocurrency depending on what currencies your NFT provider accepts, most likely Ether. You can use platforms like OpenSea, Coinbase, Kraken, PayPal, etc., to buy cryptocurrencies.
- Once you’ve made your cryptocurrency purchase, you can move it from the exchange to your wallet.
Bear in mind, that many exchanges charge a small percentage of your crypto purchase transaction as fees.
Popular NFT Marketplaces
Once you’ve got your wallet ready, all you need to do is to buy NFT. Currently, the largest NFT marketplaces are:
- Rarible - Rarible is a democratic marketplace that allows artists and creators to issue and sell NFTs. It enables holders to weigh in on features like fees and community rules.

- OpenSea - To get started, all you need to do is create an account on the official website of OpenSea and browse NFT collections and discover new artists. This platform is famously known as a vast collection of rare digital items and collectibles.

- Foundation - On this platform, artists need to receive from or send an invitation from fellow creators to post their art. This community’s exclusivity boasts higher-caliber artwork, assuming the demand for NFTs remains at current levels or even increases over time.
NFT Use Cases
Popular NFT use cases include
- Event ticketing
- Gaming
- Supply chain
- Art and collectibles
- Web3 identification
- Music
- Virtual real estate
- Food and drink
- Decentralized finance loans
- Fashion
NFT Scams
With the growing popularity of NFTs the potential for fraud and scams is also growing.
Scammers use various methods to cheat buyers. These include using false information to sell NFTs, making fake NFTs and conducting auctions without any intention of delivering the NFTs. These scams can make buyers lose a lot of money.
Creating fake NFTs or “mimic NFTs” is one of the most common scams. In this, a digital file similar to NFT is created, but it has no ownership or value and is then sold for a large amount of money.
Scammers also use false information, such as fake reviews or celebrity endorsements to create a false sense of value and authenticity.
Another scam involves scammers conducting auctions without delivering the NFTs.
To safeguard themselves, buyers should research the authenticity of the NFT and the seller and buy only from reputed sellers and marketplaces.
How are NFTs Reinventing the Digital World?
NFTs are transforming the digital world by providing a way to verify ownership and authenticate digital assets by forging new pathways for investors, creators and collectors. NFTs are unique digital assets that can represent anything from music to digital art to in-game items and virtual real estate.
One of the most important advantages of the NFTs is that the digital creators get to monetize their work which was difficult to do before. NFTs provide a way of creating verifiable ownership and scarcity, making digital art and other digital assets more collectible and valuable.
Moreover, NFTs can potentially transform the gaming market by making a new market for virtual assets. Players can now sell, trade and buy virtual items with ownership that is verifiable. This enables new economic systems within games and new forms of gameplay.
Furthermore, NFTs can create new opportunities in the music industry by enabling artists to monetize their work apart from traditional channels. NFTs can represent concert tickets, unique digital collectibles and even ownership rights of songs.
NFTs are transforming the digital world by offering new methods of monetizing and authenticating digital assets. They can create new markets and opportunities across multiple industries by making them fast-evolving technology.
How Does the Future of NFT Look Like?

NFT has enhanced media exposure and special perks for aspiring artists on social media. Recently, Jack Dorsey, the CEO and co-founder of Twitter, with his very first and famous tweet, "just setting up my twttr," and Vignesh Sundaresan, famously known as "Metakovan," bought 69.3 million dollars worth of NFT art on Beeple.
Owing to its increasing popularity, people are now willing to pay hundreds of thousands of dollars for NFTs.
Like David Gerard, author of Attack of the 50-foot Blockchain, many experts in the crypto industry say that around 40% of new crypto users will use NFTs as their entry point. As a result of its growing popularity, NFT could represent a more significant part of the digital economy in the future.
FAQs
1. What are some examples of non-fungible tokens?
NFTs can represent any asset digitally. It can be online-only assets such as digital artwork or real assets like real estate. Some examples are in-game avatars, digital/ non-digital collectibles, tickets, domain names, and more.
2. How can I buy NFTs?
Most non-fungible tokens can be purchased with Ether only. So, owning and storing them in a digital wallet is the primary step. You can buy NFTs via an online NFT marketplace such as OpenSea, SuperRare, and Rarible.
3. Are NFTs safe?
NFTs that use blockchain technology like cryptocurrency are generally secure. Their distributed nature makes NFTs nearly impossible to hack. The only security risk is that you could lose access to your NFTs if the hosting platform goes out of business.
4. What does non-fungible mean?
Fungibility is a term from economics describing the interchangeability of products/ goods. For instance, an item such as a dollar bill is fungible when it is interchangeable with any other dollar bill. Contrastingly, non-fungible means the item is unique or distinguishable. For example, if you take a dollar bill and have it signed by a famous artist, it will become unique.
5. What are NFTs, exactly?
NFTs or non-fungible tokens are digital assets based on blockchain technology. Anything can become an NFT—a piece of art, sports memorabilia, or even a tweet.
6. What are NFTs used for?
NFTs are digital files. They can be a jpeg of a piece of art, real estate, or a video. Turning files into NFTs helps secure them via blockchain to make buying, selling and trading efficient, reducing fraud considerably.
7. How do NFTs and crypto connect?
Like cryptocurrencies, non-fungible tokens also exist on a blockchain. It confirms the ownership and unique identity of the digital asset. A technology similar to Bitcoin and Ethereum is used to build NFTs. In fact, Ethereum is the widely accepted crypto in the NFT market.
8. Why do people buy NFTs?
NFTs are considered a safe investment option. These tokenized assets are accessible to everyone. They empower you with basic usage rights. Moreover, most buyers invest in them because they believe the assets will hold value in the future.
9. What are the best ways to make money from NFTs?
Some of the best ways to maximize the return from NFTs include Renting, Earning royalties, Trading NFTs, NFT gaming and Adopting NFT-powered yield farming.
10. Should I invest in an NFT?
Experts suggest that NFTs can be a good investment because you can resell them for profit. Several NFT marketplaces allow sellers to get royalties for their sold assets. However, proper research is necessary before investing so that you can gauge whether it suits your demands.
11. What's the difference between NFTs and cryptocurrency?
Both cryptocurrencies and NFTs use the blockchain network for ownership verification. However, unlike a cryptocurrency, an NFT can't be directly exchanged with another NFT. NFTs are sold but not traded like securities on digital exchanges. In contrast, cryptocurrencies can be traded like securities.
12. What is NFT digital art and how does NFT art work?
NFT art is digital art tokenized in the blockchain, much like any other NFT object. Since the artwork is totally digital, buyers, sellers, and traders eventually transact in the metaverse. NFT art also has a single original, just like there is with physical art.
Conclusion
Thanks to this “What is an NFT?” tutorial, you have now seen everything you need to know about what an NFT is, how it works, its uses, and how you can buy them.
Whether you're an experienced Blockchain developer or just an enthusiast who wants to explore more about NFTs, cryptocurrencies, and blockchain, you can enroll in Simplilearn's Professional Certificate Program in Blockchain. This program helps you learn and explore more about cryptocurrencies, blockchain, and all the associated technology, accommodating all levels of experience.
Do you have any questions for us? Please feel free to drop them in the comments section of this article, and our experts will get back to you as soon as possible.


